General surgery
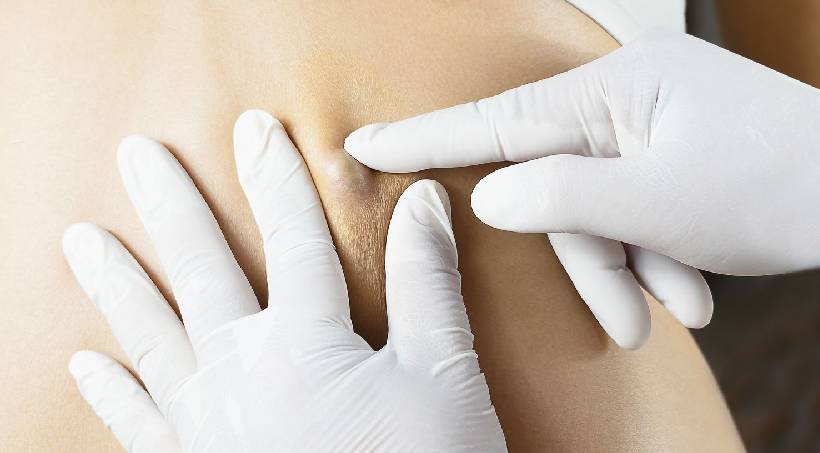
Sebaceous cysts are a common occurrence that many individuals encounter at some point in their lives. These cysts may appear alarming, but they are generally harmless growths that develop beneath the skin. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for sebaceous cysts, providing valuable insights in easy-to-understand terms.
What is a Sebaceous Cyst?
A sebaceous cyst, also known as an epidermoid cyst, is a noncancerous growth that forms beneath the skin. These cysts typically arise from hair follicles or oil glands, known as sebaceous glands, which produce an oily substance called sebum. Sebaceous cysts occur when sebum becomes trapped within a sac-like structure beneath the skin, leading to the formation of a lump or bump.
Causes of Sebaceous Cysts:
Several factors contribute to the development of sebaceous cysts:
- Blocked Glands: Sebaceous cysts often occur when the ducts or openings of the sebaceous glands become blocked, preventing the natural flow of sebum to the skin’s surface.
- Trauma or Injury: Physical trauma or injury to the skin can also trigger the formation of sebaceous cysts by causing damage to the hair follicles or sebaceous glands.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can increase the production of sebum and predispose individuals to sebaceous cysts.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing sebaceous cysts, making them more susceptible to these growths.
Symptoms of Sebaceous Cysts:
Sebaceous cysts typically present as small, round bumps beneath the skin’s surface. Key symptoms include:
- Visible Lump or Bump: The most common sign of a sebaceous cyst is a visible lump or bump that may be white, yellowish, or flesh-colored. These cysts are often smooth to the touch and may vary in size.
- Painless Swelling: Sebaceous cysts are usually painless unless they become infected or inflamed. However, they may cause discomfort if they press on nearby nerves or tissues.
- Redness and Tenderness: If a sebaceous cyst becomes infected, it may appear red, swollen, and tender to the touch. In some cases, the cyst may discharge pus or a foul-smelling fluid.
- Gradual Growth: Sebaceous cysts may grow slowly over time, increasing in size and becoming more noticeable.
Diagnosis of Sebaceous Cysts:
Diagnosing a sebaceous cyst typically involves a thorough examination by a healthcare professional. Your doctor will assess the appearance, size, and location of the cyst, as well as any associated symptoms. In some cases, additional tests or procedures may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis, including:
- Physical Examination: Your doctor will examine the cyst and may gently palpate it to assess its size, texture, and tenderness.
- Medical History: Providing details about your medical history, including any previous skin conditions or treatments, can help your doctor determine the underlying cause of the cyst.
- Imaging Studies: In certain cases, imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI may be ordered to visualize the internal structures of the cyst and rule out any underlying complications.
- Biopsy: In rare instances where the diagnosis is uncertain or there is concern about malignancy, a biopsy may be performed. During a biopsy, a small tissue sample is removed from the cyst and examined under a microscope to determine the nature of the growth.
Treatment Options for Sebaceous Cysts:
Sebaceous cysts often do not require treatment unless they become symptomatic or cosmetically bothersome. However, if intervention is necessary, several treatment options are available:
- Watchful Waiting: In many cases, sebaceous cysts are harmless and may resolve on their own without intervention. Your doctor may recommend a wait-and-watch approach, monitoring the cyst for any changes in size, shape, or symptoms.
- Incision and Drainage: If a sebaceous cyst becomes infected or inflamed, your doctor may perform a minor surgical procedure known as incision and drainage. During this procedure, the cyst is numbed with local anesthesia, and a small incision is made to drain the fluid and relieve pressure. Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat any underlying infection.
- Injection of Corticosteroids: Inflammation associated with sebaceous cysts can be reduced by injecting corticosteroids directly into the cyst. This treatment helps alleviate pain and swelling and may prevent recurrence.
- Surgical Excision: Surgical excision involves removing the entire cyst and its surrounding capsule through a minor surgical procedure. This option is typically recommended for large, recurrent, or cosmetically bothersome cysts. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, and stitches may be used to close the incision.
Prevention of Sebaceous Cysts:
While it may not be possible to prevent sebaceous cysts entirely, several strategies can help minimize the risk of their development:
- Practice Good Hygiene: Maintaining proper hygiene by washing the skin regularly with a gentle cleanser can help prevent the buildup of oil, dirt, and debris that contribute to blocked glands.
- Avoid Squeezing or Picking: Refrain from squeezing, picking, or attempting to drain sebaceous cysts at home, as this can lead to infection, scarring, and potential complications.
- Protective Measures: Take precautions to protect the skin from trauma or injury, especially in areas prone to friction or pressure. Use protective padding or clothing to minimize the risk of skin irritation.
- Manage Hormonal Imbalances: If you experience hormonal fluctuations or imbalances, consult with your healthcare provider to explore treatment options that can help regulate hormone levels and reduce the risk of cyst formation.
Conclusion:
Sebaceous cysts are common benign growths that can occur anywhere on the body. While they are generally harmless, they may cause discomfort or concern, especially if they become infected or inflamed. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for sebaceous cysts is essential for effective management and prevention of complications. If you have any concerns about a skin growth or lesion, it is important to seek prompt medical attention from a qualified healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.

