Laparoscopic surgery
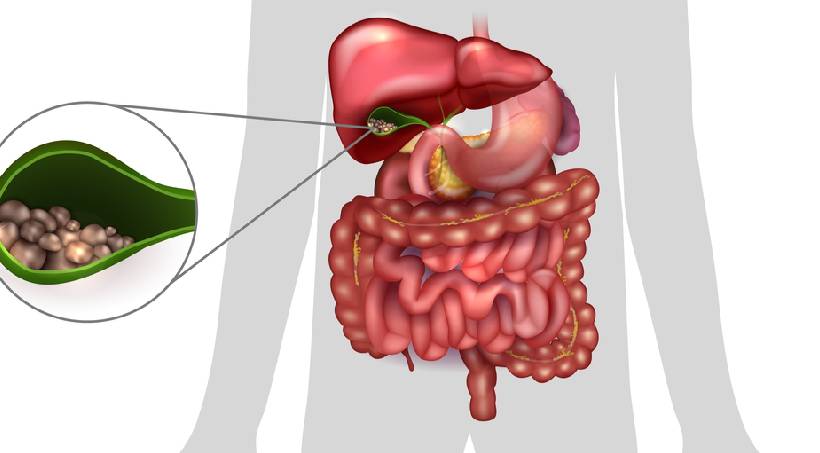
Introduction to Gallstones:
Gallstones are small, pebble-like substances that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. They can vary in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. Gallstones develop when there is an imbalance in the substances that make up bile, a digestive fluid stored in the gallbladder.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for gallstones, aimed at providing a clear understanding for the common person.
- Causes of Gallstones:
Gallstones develop when there is an imbalance in the components of bile, particularly cholesterol and bilirubin. Several factors contribute to the formation of gallstones:- Excess Cholesterol: When the bile contains too much cholesterol and not enough bile salts or lecithin to keep it in a liquid state, cholesterol can crystallize and form stones.
- Bilirubin Imbalance: Excessive breakdown of red blood cells can lead to an increased level of bilirubin, contributing to gallstone formation.
- Gallbladder Emptying Problems: If the gallbladder fails to empty completely or if it doesn’t empty often enough, bile may become concentrated, promoting the formation of gallstones.
- Other Risk Factors: Obesity, rapid weight loss, a diet high in fat and cholesterol, certain medications, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and liver disease can increase the risk of developing gallstones.
- Symptoms of Gallstones:
Gallstones may not always cause symptoms, but when they do, the symptoms can be severe and disruptive. Common symptoms of gallstones include:- Pain: The most common symptom of gallstones is sudden and intense pain in the upper right abdomen, often radiating to the back or right shoulder. This pain, known as biliary colic, can last from several minutes to several hours.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Gallstone pain may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Indigestion and Heartburn: Some individuals may experience indigestion, bloating, or heartburn after eating fatty or greasy foods.
- Jaundice: If a gallstone blocks the bile duct, it can lead to jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Fever and Chills: In some cases, gallstones can cause inflammation or infection in the gallbladder, leading to fever and chills.
- Diagnosis of Gallstones:
If gallstones are suspected based on symptoms, a healthcare provider may order several diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis:- Ultrasound: An abdominal ultrasound is the most common test used to visualize the gallbladder and detect the presence of gallstones.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to check for signs of inflammation, infection, or jaundice.
- CT Scan or MRI: In some cases, a CT scan or MRI may be ordered to get detailed images of the gallbladder and surrounding structures.
- Cholescintigraphy (HIDA scan): This nuclear medicine scan helps evaluate the function of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
- Treatment Options for Gallstones:
Treatment for gallstones depends on the severity of symptoms and the risk of complications. Options may include:- Watchful Waiting: If gallstones are small and not causing symptoms, a healthcare provider may recommend a wait-and-see approach, monitoring for any changes or symptoms.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as oral bile acid pills, may be prescribed to dissolve cholesterol gallstones over time.
- Surgery: If gallstones are causing severe symptoms or complications, surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) may be recommended. This procedure is typically performed laparoscopically and is considered safe and effective.
- Endoscopic Procedures: In some cases, gallstones can be removed using endoscopic techniques, such as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC).
- Prevention of Gallstones:
While not all gallstones can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes may help reduce the risk of developing gallstones:- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Aim to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: Limit consumption of high-fat, high-cholesterol foods, and focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help prevent the concentration of bile.
- Avoid Rapid Weight Loss: Gradual weight loss is preferable to rapid weight loss, which can increase the risk of gallstone formation.
Conclusion:
Gallstones are a common condition that can cause significant discomfort and complications if left untreated. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for gallstones, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and reduce the risk of developing gallstones in the future. If experiencing symptoms suggestive of gallstones, it is essential to seek prompt medical attention for proper evaluation and treatment.

